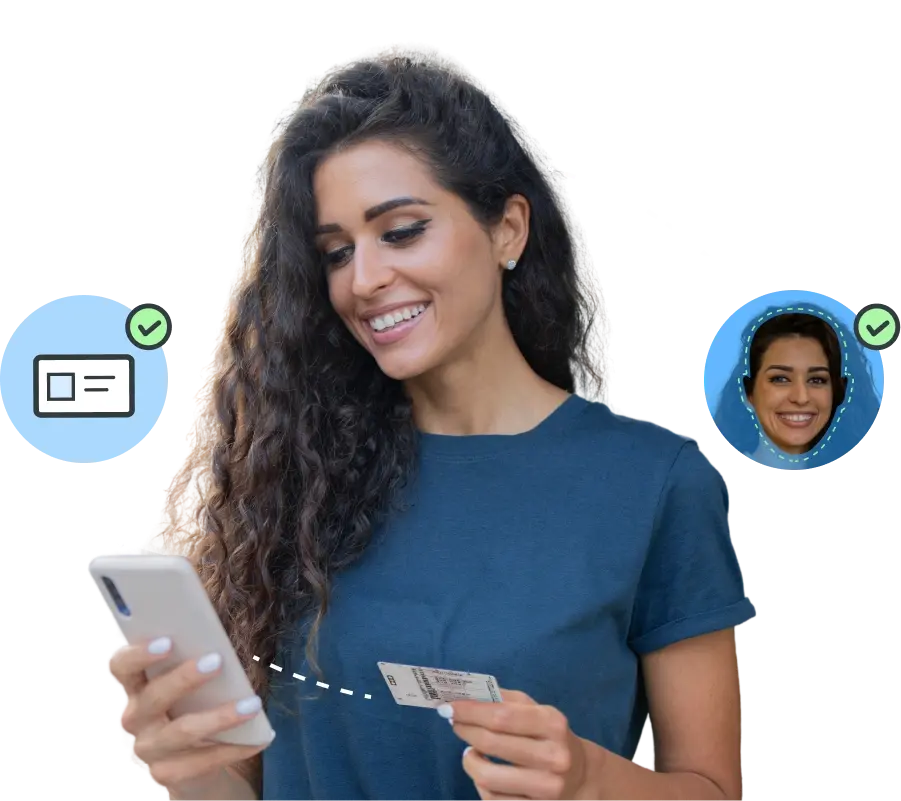
All the customer verification solutions you need to comply with regulations in one platform.
Yoti is a pioneer in reusable Digital ID wallets and is a market leader in age assurance technology. We have world class automated document verification with anti-spoofing, deepfake protection and expert human review when required.
How Yoti can help your business beat fraud and build trust
-
Over
10m
checks
every month -
95%
Success
rate -
20m
Digital ID
wallet downloads
-
Over
10m
checks
every month -
95%
Success rate -
20m
Digital ID
wallet downloads
-
Over
10m
checks
every month -
95%
Success
rate -
20m
Digital ID
wallet downloads
How to get started with Yoti
Web portal
No integration required. Send and review identity check requests in seconds.
Developer hub
Use our APIs and SDKs to build the solution that works for you. Easy to use with support available from our integrations team.

Built with security and privacy as a priority
Our systems are built in a way that means we cannot mine or sell data to third parties. Once we’ve completed our security checks, we can’t access any user details. We’re trusted by regulators for adhering to the highest standards of security.
Building trust for market leaders
Yoti excels in building robust verification solutions for regulated businesses and governments
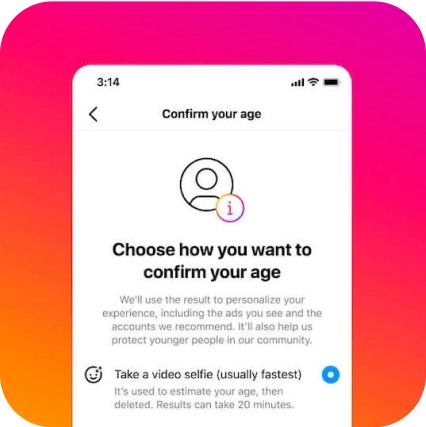
Giving Instagram new ways to verify age
Instagram uses Yoti's facial age estimation technology as an option for people who need to prove they are over 18 on Instagram. Over 80% of people choose facial age estimation.

Striving to do the right thing, from day one
We were founded on a robust framework that ensures we continue to drive the development of ethical technology. We work with regulators around the world to inform and progress vital standards to make the internet a safer place for everyone.
As a certified B Corp, we aim to place equal value on people, planet, purpose and profit. From the start, we’ve been committed to a transparent, honest and inclusive approach to making identity accessible to everyone.











